Have you ever wondered where humans fit into the vast web of life on Earth? From microscopic cells to complex ecosystems, our place in the natural world is both fascinating and unique. Discover how we are classified in the grand hierarchy of life and what makes us truly special among all living beings.
Section 1: Human Classification in the Natural World
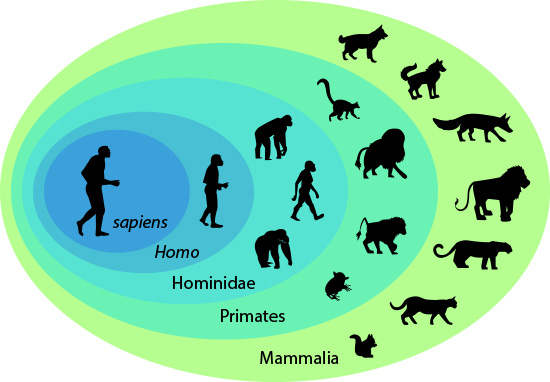
Organisms on Earth are classified using a hierarchical system that organizes life based on shared characteristics. This system consists of eight major levels: domain, kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, and species.
Domains of Life
There are three domains of life:
- Bacteria – Single-celled prokaryotic organisms with no nucleus.
- Archaea – Also single-celled prokaryotes, but distinct from bacteria in genetic makeup and biochemistry, often found in extreme environments.
- Eukaryota – Organisms with complex cells that have a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles.

Humans belong to the domain Eukaryota, as our cells have a nucleus and organelles. Within Eukarya, we are further classified into:
- Kingdom: Animalia – Multicellular organisms that are heterotrophic (consume organic material for energy), have complex tissues, and exhibit movement.
- Phylum: Chordata – Animals that have a notochord (a flexible rod supporting the body), a dorsal nerve cord, and pharyngeal slits at some stage of development.
- Class: Mammalia – Warm-blooded animals with hair or fur, mammary glands for milk production, and three middle ear bones.
- Order: Primates – Mammals with large brains, forward-facing eyes for depth perception, and grasping hands.
- Family: Hominidae – The great apes, including humans, chimpanzees, gorillas, and orangutans.
- Genus: Homo – Characterized by larger brain sizes and upright walking.
- Species: Homo sapiens – The only surviving human species, distinguished by advanced cognitive abilities, culture, and language.
Subscribe our Youtube channel @wiladio for more interesting video about Design, Science, Tech, and Game

Section 2: Defining Features of Humans
Humans possess several defining biological and behavioral traits that set us apart from other species:
- Bipedalism – Humans walk upright on two legs, which frees the hands for tool use and allows for long-distance travel.
- Opposable Thumbs – Our thumbs can touch the tips of other fingers, allowing for precise gripping and manipulation of objects.
- Large Brain – Humans have a highly developed cerebral cortex, enabling complex problem-solving, abstract thinking, and technological advancements.
- Capacity for Complex Language – Unlike other primates, humans have sophisticated spoken and written language, which enables culture, cooperation, and knowledge transmission.

Section 3: Levels of Biological Organization in Humans
Biologists study humans at different levels of organization, from the smallest chemical units to interactions with the environment:
- Atom and Molecule – The basic chemical building blocks of life, including carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, which form molecules like DNA and proteins.
- Cell – The fundamental unit of life; humans are composed of trillions of eukaryotic cells.
- Tissue – Groups of similar cells working together, such as muscle tissue or nervous tissue.
- Organ – Structures composed of different tissues, such as the heart, lungs, and brain, that perform specific functions.
- Organ System – Groups of organs working together, such as the circulatory system (heart and blood vessels) and nervous system (brain and nerves).
- Organism – A complete, living human being functioning as an independent unit.
- Population – Groups of humans living in a specific area and interacting with one another.
- Community – The interaction of human populations with other living organisms in an area.
- Ecosystem – The interaction of all living and non-living elements (such as climate and geography) in an environment.
- Biosphere – The global sum of all ecosystems, where all life on Earth exists.
Conclusion
Humans occupy a unique place in the natural world, classified within the domain Eukarya and further categorized down to the species Homo sapiens. Our defining biological features, including bipedalism, intelligence, and language, distinguish us from other species. Additionally, humans can be studied across multiple levels of biological organization, from molecules to the entire biosphere, highlighting the complexity of life.
THE END
More Science articles: https://wiladio.com/category/science/












